View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Large Flowered Beardtongue - Penstemon grandiflorus
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Rare in Montana, where it is known from only a few sites on the plains of eastern Montana.
General Description
Large Flowered Beardtongue is a stout perennial herb with 1-2 erect stems that are 5-10 dm tall and arising from a taproot surmounted by a woody, usually unbranched crown. The spoon- to egg-shaped basal leaves are 3-16 cm long and have petioles and entire margins. The opposite, clasping stem leaves are shorter and broadly oblong. Foliage is glabrous, thickish, and covered with a thin, bluish wax. The inflorescence consists of 3-7 clusters of 2-4 short-stalked flowers in the axils of the reduced upper leaves. The tubular corolla is flared and 2-lipped at the mouth, 35-48 mm long, and pink to lavender or pale blue. The 5 broadly lance-shaped calyx segments are 7-11 mm long and usually green throughout. The 4 anthers are glabrous.
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting April-July.
Diagnostic Characteristics
The combination of exceptionally large flowers and glabrous inflorescence and anthers distinguish this species from others in Penstemon. It most closely resembles P. nitidus but the latter has a corolla less than 20 mm long. A hand lens may be required for identification.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions

 Native
Native
Range Comments
MT to IN, south to TX. One collection from Custer County; a collection from Phillips County represents a reclamation planting (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 6
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density

Recency
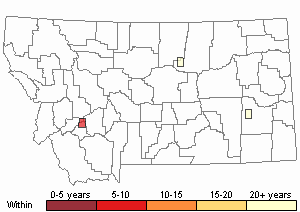


 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Sandy soil of valleys on the plains.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus appositus,
Bombus auricomus,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus impatiens,
Bombus insularis,
Bombus suckleyi,
Bombus bohemicus, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Macior 1974, Thorp et al. 1983, Bauer 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Wilson et al. 2010, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Pyke et al. 2012, Miller-Struttmann and Galen 2014, Williams et al. 2014, Tripoldi and Szalanski 2015).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
STATE THREAT SCORE REASON
Threat impact not assigned because threats are not known (MTNHP Threat Assessment 2021).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144.
Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144. Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59.
Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045.
Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045. MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349.
Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834
Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834 Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Heidel, B. L. 1996. Noteworthy collections - Montana. Madrono 43(3):436-440.
Heidel, B. L. 1996. Noteworthy collections - Montana. Madrono 43(3):436-440. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Strickler, D. 1997. Northwest penstemons. Flower Press, Columbia Falls, Montana. 191 pages.
Strickler, D. 1997. Northwest penstemons. Flower Press, Columbia Falls, Montana. 191 pages.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Large Flowered Beardtongue"





