View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
White Spiraea - Spiraea betulifolia
Other Names:
Spiraea lucida, Spiraea betulifolia var. lucida
General Description
Rhizomatous. Stems 20–80 cm, glabrous, reddish-brown, shredding with age. Leaf blades 2–9 cm long, glabrous, serrate above, basally entire, green above, paler beneath. Inflorescence flat-topped, glabrous, 3–15 cm across. Flowers: sepals <1 mm long, glabrous; petals white, ca. 2 mm long. Follicles 3 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Our plants are variety
lucida (Douglas ex Greene) C.L. Hitchc.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Pyramidal Spiraea is a natural hybrid between
Spiraea douglasii var.
menziesii and
Spiraea betulifolia var.
lucida, which are all present in Montana.
White Spirea –
Spiraea betulifolia, native:
* Inflorescence is flat-topped to hemispheric, broader than long.
* Flowers are white.
* Leaves are glabrous.
* Montana’s variety is
lucida.
Douglas Spirea –
Spiraea douglasii, native:
* Inflorescence is cone-shaped, at least three times longer than broad.
* Flowers are pink to rose.
* Montana’s variety is
menziesii.
Pyramidal Spiraea –
Spiraea x
pyramidata, native hybrid:
* Inflorescence is cone-shaped, about as long as broad or up to twice as long as broad.
* Flowers are pink-tinged.
Rose Meadowsweet –
Spiraea splendens, native:
* Inflorescence is flat-topped to hemispheric, broader than long.
* Flowers are rose.
* Leaves are hairy on the margins.
Source: Lesica et al. (2012).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
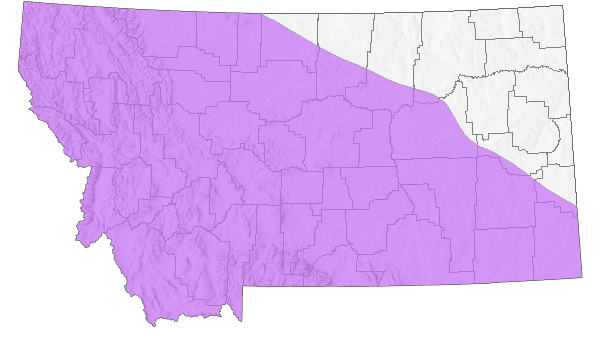
 Native
Native
Range Comments
BC to SK south to OR, WY and SD (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
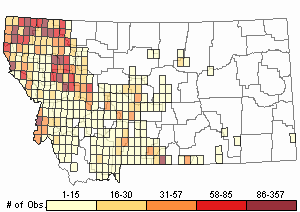
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 7097
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
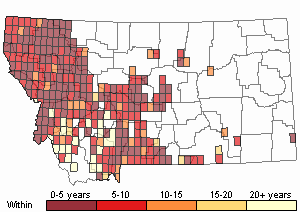
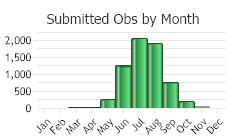
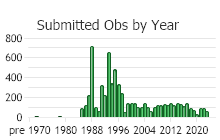
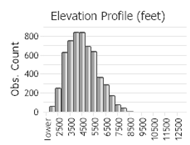 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus auricomus,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus ternarius,
Bombus griseocollis, and
Bombus impatiens (Macior 1968, Heinrich 1976, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25.
Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p.
Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p. Aradottir, A.L. 1984. Ammonia volatilization from native grasslands and forests of SW Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 48 p.
Aradottir, A.L. 1984. Ammonia volatilization from native grasslands and forests of SW Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 48 p. Bradley, A. F. 1984. Rhizome morphology, soil distribution, and the potential fire survival of eight woody understory species in western Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 184 pp.
Bradley, A. F. 1984. Rhizome morphology, soil distribution, and the potential fire survival of eight woody understory species in western Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 184 pp. Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp.
Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp. Conway, T.M. 1982. Response of understory vegetation to varied lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) spacing intervals in Western Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bpzeman, MT: Montana State University. 76 p.
Conway, T.M. 1982. Response of understory vegetation to varied lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta) spacing intervals in Western Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bpzeman, MT: Montana State University. 76 p. Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p.
Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p. Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp.
Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp. Dale, D. 1973. Effects of trail use under forests in the Madison Range, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 96 pp.
Dale, D. 1973. Effects of trail use under forests in the Madison Range, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 96 pp. Dresser, M.A. 2015. Demographic responses of woodpeckers in relation to a Mountain Pine Beetle epidemic in the Elkhorn Mountains of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 71 p.
Dresser, M.A. 2015. Demographic responses of woodpeckers in relation to a Mountain Pine Beetle epidemic in the Elkhorn Mountains of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 71 p. Eversman, S.T. 1968. A comparison of plant communities and substrates of avalanche and non-avalanche areas in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 pp.
Eversman, S.T. 1968. A comparison of plant communities and substrates of avalanche and non-avalanche areas in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 pp. Fogelsong, M.L. 1974. Effects of fluorides on Peromyscus maniculatus in Glacier National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 52 p.
Fogelsong, M.L. 1974. Effects of fluorides on Peromyscus maniculatus in Glacier National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 52 p. Forcella, F. 1977. Flora, chorology, biomass and productivity of the Pinus albicaulis-Vaccinium scoparium association. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 99 pp.
Forcella, F. 1977. Flora, chorology, biomass and productivity of the Pinus albicaulis-Vaccinium scoparium association. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 99 pp. Fultz, J.E. 2005. Effects of shelterwood management on flower-visiting insects and their floral resources. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 163 p.
Fultz, J.E. 2005. Effects of shelterwood management on flower-visiting insects and their floral resources. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 163 p. Habeck, R. J. 1991. Spiraea betulifolia. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online}. U. S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer).
Habeck, R. J. 1991. Spiraea betulifolia. In: Fire Effects Information System, [Online}. U. S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory (Producer). Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p.
Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p. Hodgson, J.R. 1970. Ecological distribution of Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus in an area of geographic sympatry in southwestern Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 65 p.
Hodgson, J.R. 1970. Ecological distribution of Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus in an area of geographic sympatry in southwestern Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 65 p. Jensen, P.D. 2001. The foraging and nesting behavior of four solitary-nesting bee species (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae) in the Gallatin Valley, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 76 p.
Jensen, P.D. 2001. The foraging and nesting behavior of four solitary-nesting bee species (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae) in the Gallatin Valley, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 76 p. Johnson, T. W. 1982. An analysis of pack and saddle stock grazing areas in the Bob Marshall Wilderness. M.Sc.Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 105 p.
Johnson, T. W. 1982. An analysis of pack and saddle stock grazing areas in the Bob Marshall Wilderness. M.Sc.Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 105 p. Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp.
Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp. Joslin, G.J. 1975. Behavior and environmental selection by Elk (Cervus canadensis nelsoni) during surrmer and fall in the First and Second Yellow Mule drainages, Madison County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University, Bozeman. 65 p.
Joslin, G.J. 1975. Behavior and environmental selection by Elk (Cervus canadensis nelsoni) during surrmer and fall in the First and Second Yellow Mule drainages, Madison County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University, Bozeman. 65 p. Klebenow, D.A. 1965. A montane forest winter deer habitat in western Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 29(1):27-33.
Klebenow, D.A. 1965. A montane forest winter deer habitat in western Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 29(1):27-33. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Lovaas, A.L. 1957. Mule deer food habits and range use in the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p.
Lovaas, A.L. 1957. Mule deer food habits and range use in the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p. Martinka, R.R. 1970. Structural characteristics and ecological relationships of male blue grouse (Dendragapus obscurus (Say)) territories in southwestern Montana. Ph.D Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 73 p.
Martinka, R.R. 1970. Structural characteristics and ecological relationships of male blue grouse (Dendragapus obscurus (Say)) territories in southwestern Montana. Ph.D Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 73 p. Meier, G.A. 1997. The colonization of Montana roadsides by native and exotic plants. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p.
Meier, G.A. 1997. The colonization of Montana roadsides by native and exotic plants. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p. Morgan, J.T. 1993. Summer habitat use of white-tailed deer on the Tally Lake ranger district, Flathead National Forest. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. pp. 103.
Morgan, J.T. 1993. Summer habitat use of white-tailed deer on the Tally Lake ranger district, Flathead National Forest. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. pp. 103. Plaggemeyer, J.B. 1995. Effects of overstory thinning on lodgepole pine understories. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 55 p.
Plaggemeyer, J.B. 1995. Effects of overstory thinning on lodgepole pine understories. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 55 p. Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p.
Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p. Schubloom, L.A. 1995. Lichens as air quality indicators in three areas of southwestern Montana: lichen floristics and elemental analysis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 130 p.
Schubloom, L.A. 1995. Lichens as air quality indicators in three areas of southwestern Montana: lichen floristics and elemental analysis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 130 p. Sikes, D.S. 1994. Influences of ungulate carcasses on Coleopteran communities in Yellowstone National Park, USA. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 179 p.
Sikes, D.S. 1994. Influences of ungulate carcasses on Coleopteran communities in Yellowstone National Park, USA. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 179 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445. Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p.
Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "White Spiraea"





