View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Corn-gromwell - Lithospermum arvense
Other Names:
Field Gromwell, Bastard Alkanet,
Buglossoides arvensis
General Description
Taprooted annual. Stems erect, 10–70 cm, usually branched. Herbage strigose. Leaves linear-oblong, 2–5 cm long, the lowest withered at flowering. Inflorescence becoming open; pedicels short. Flowers: calyx 4–5 mm long; corolla white, sometimes bluish, 5–8 mm long with longitudinal lines of hair within the tube, 3–4 mm across the limb; fornices absent; style included. Nutlets 2.5–4 mm long, rugose; scar umrimmed (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Non-native
Non-native
Range Comments
Introduced throughout most of temperate North America; native to Eurasia (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
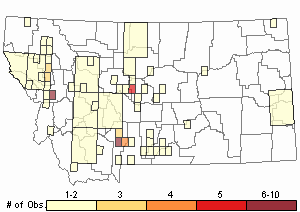
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 133
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
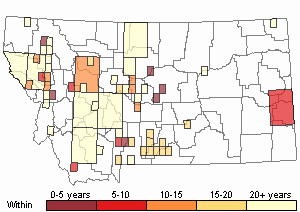
Recency
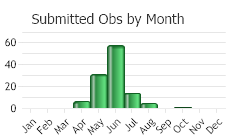
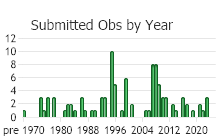
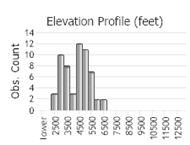 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus pensylvanicus and
Bombus impatiens (Colla and Dumesh 2010).
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Adhikari, S. 2018. Impacts of dryland farming systems on biodiversity, plant-insect interactions, and ecosystem services. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 207 p.
Adhikari, S. 2018. Impacts of dryland farming systems on biodiversity, plant-insect interactions, and ecosystem services. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 207 p. Douglass, R.J. 1973. Spatial interactions and microhabitat selections of two locally sympatric voles, Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 48 p.
Douglass, R.J. 1973. Spatial interactions and microhabitat selections of two locally sympatric voles, Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 48 p. Harvey, A.J. 2019. Understanding the biology, ecology, and integrated management of Ventenata dubia. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 117 p.
Harvey, A.J. 2019. Understanding the biology, ecology, and integrated management of Ventenata dubia. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 117 p. Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp.
Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Lovaas, A.L. 1957. Mule deer food habits and range use in the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p.
Lovaas, A.L. 1957. Mule deer food habits and range use in the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p. Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p. Seipel, T.F. 2006. Plant species diversity in the sagebrush steppe of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 87 p.
Seipel, T.F. 2006. Plant species diversity in the sagebrush steppe of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 87 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Corn-gromwell"





