View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Bitter Fleabane - Erigeron acris
Other Names:
Trimorpha acris, Erigeron kamtschaticus, Erigeron nivalis
General Description
Short-lived, tap- or fibrous-rooted perennial. Stems ascending to erect, 5–60 cm. Herbage sparsely hirsute; stipitate-glandular. Leaves basal and cauline; blades oblanceolate, 2–10 cm long, entire, narrower and sessile above. Heads 1 to 30, radiate. Involucres hemispheric, 4–8 mm high; phyllaries in 2 to 3 series, glandular, hirsute, sometimes purple. Rays white to pink, 40 to 50; ligules erect, filiform, 3–5 mm long. Disk corollas 4–5 mm long. Achenes ca. 2 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Our plants are variety
debilis A. Gray and
kamtschaticus (DC.) Herder
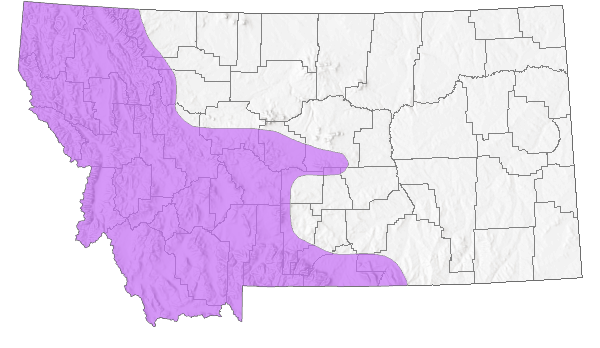
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Circumboreal south to CA, CO, MN and ME (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
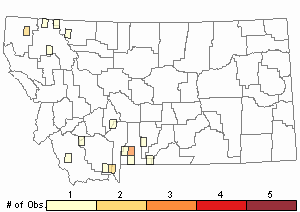
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 24
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
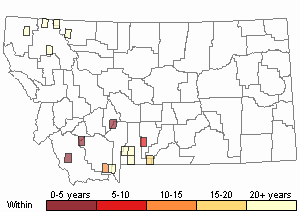
Recency
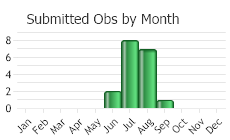
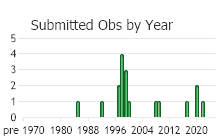
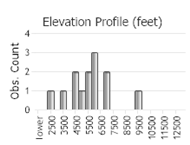 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus occidentalis, and
Bombus insularis (Thorp et al. 1983, Wilson et al. 2010, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Koch et al. 2012).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p.
Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p. Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp.
Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Martinka, R.R. 1970. Structural characteristics and ecological relationships of male blue grouse (Dendragapus obscurus (Say)) territories in southwestern Montana. Ph.D Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 73 p.
Martinka, R.R. 1970. Structural characteristics and ecological relationships of male blue grouse (Dendragapus obscurus (Say)) territories in southwestern Montana. Ph.D Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 73 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Bitter Fleabane"





