View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Yellow Dotted Alpine - Erebia pawloskii
Other Names:
Theano Alpine,
Erebia pawlowskii
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001] Forewing 1.7-2.1 cm. Small and dark brown. Both surfaces of forewing with postmedian band of rectangular red-orange spots (no black eyespots), a reddish patch in middle of wing; hindwing undersurface with 1 blurred cell spot and postmedian series of yellow-cream spots.
Phenology
One flight; mostly July in the north, mid-July to early August in the south, flying only every other year (Scott 1986). Mainly July to mid-August (Glassberg 2001). Early June through mid-August in the Rocky Mountain states (Ferris and Brown 1981), July in British Columbia (Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by both surfaces of forewing with postmedian band of rectangular red-orange spots (no black eyespots), a reddish patch in middle of wing; hindwing undersurface with 1 blurred cell spot and postmedian series of yellow-cream spots.
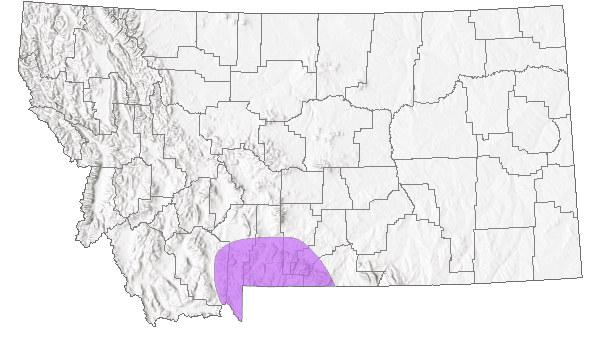
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Holarctic. In North America, fragmented and local populations in Alaska and Yukon, south in the Rocky Mountains through British Columbia to Montana, Wyoming, and Colorado; also along Hudson Bay in northern Manitoba (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001); 3230 m to 3962 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957). In Montana, reported from three southern counties (Carbon, Park, Stillwater) near Wyoming (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993), to at least 3048 m elevation (Ferris and Brown 1981). Locally uncommon (Glassberg 2001).
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 4
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
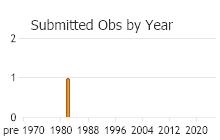
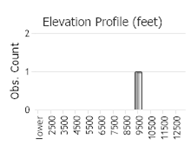 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Dry or moist tundra above or north of treeline, grassy areas, taiga, subalpine wet grassy meadows, spruce bogs (Ehrlich 1956; Oosting and Parshall 1978; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Guppy and Shepard 2001). Habitat in Montana not describe but probably alpine tundra and subalpine meadows (Ferris and Brown 1981).
Food Habits
Limited information. Larval food plants include Poa, possibly Carex, Festuca, and other grasses (Scott 1992). Adults feed on flower nectar, including Achillea, Antennaria, Astragalus, Epilobium, Oxytropis, Sedum, and Solidago (Oosting and Parshall 1978; Scott 1986, 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Limited information. Females lay eggs singly on dead blades of grass, sedge, rush near probable host plant, sometimes on willow (Scott 1986, 1992). Larvae eat leaves, build no nest. Biennial, hibernating first winter as young (L1 or L2 instar?) and second winter as nearly mature (L5 instar?) larvae (Scott 1979, 1986, 1992). Males perch and patrol slowly low above grassy swales, hillsides, bogs throughout the day in search of females (Scott 1975b, 1986).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Ehrlich, P.R. 1956. Ecological observations on Erebia (Lepidoptera: Satyridae) on northwestern America. Entomological News 67: 29-36.
Ehrlich, P.R. 1956. Ecological observations on Erebia (Lepidoptera: Satyridae) on northwestern America. Entomological News 67: 29-36. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Oosting, D.P. and D.K. Parshall. 1978. Ecological notes on the butterflies of the Churchill region of northern Manitoba. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(3): 188-203.
Oosting, D.P. and D.K. Parshall. 1978. Ecological notes on the butterflies of the Churchill region of northern Manitoba. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(3): 188-203. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1979. Hibernal diapause of North American Papilionoidea and Hesperioidea. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 18(3): 171-200.
Scott, J.A. 1979. Hibernal diapause of North American Papilionoidea and Hesperioidea. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 18(3): 171-200. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Yellow Dotted Alpine"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





