View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Sonoran Skipper - Polites sonora
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Pyle 2002] Forewing 1.2-1.3 cm. Fringe grayish-white, uncheckered. Uppersurface reddish-brown to orange, dark areas with orange overscaling, blackish male stigma long and broad, narrow postmedian band of cream spots, pair of postbasal spots; undersurface of hindwing gray-green (subspecies in Montana) to orange-tan to red-brown, with narrow postmedian band of yellow-cream spots and a pair of postbasal spots.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a list, with synonymies, of 13,055 described native, exotic, and occasional straying Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico; known but undescribed taxa, taxa with unresolved taxonomy, and excluded species are also included. The
main manuscript includes links to supplementary materials, including a reference list for Lepidoptera of North America north of Mexico, and a filterable spreadsheet with information on taxonomy, synonymy, size ranges of species, distribution by state, province, and country with references, and host-plant Family and Genus associations with references.
Phenology
One flight, mostly late June to mid-August, mid-July to mid-August in Colorado (Scott 1986). Late May to August (Glassberg 2001). Mid-July to mid-August in the Rocky Mountain states (Ferris and Brown 1981). Early July to late August in Colorado (Emmel 1964; Scott and Scott 1978), early May to early September in California (Langston 1974), late May to late August in Oregon and Washington (Pyle 2002; Warren 2005), mid-July to mid-August in British Columbia (Layberry et al. 1998; Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by a combination of upper wing color, blackish male stigma elongate and broad, undersurface of hindwing gray-green for subspecies in Montana, with narrow postmedian band of yellow-cream spots and a pair of postbasal spots.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
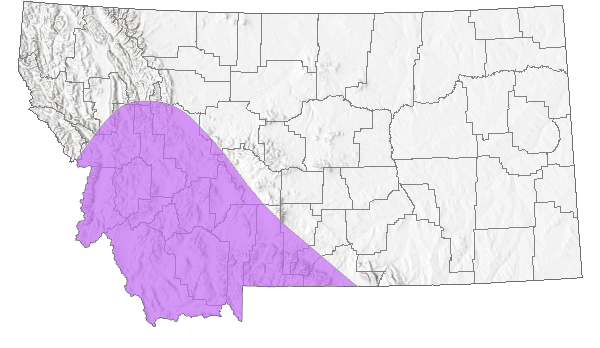
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Southern British Columbia east to southwestern Montana, south to southern California, northern Arizona, southern Colorado; also to northern Baja California (Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Guppy and Shepard 2001); 2195 m to 3200 m elevation in the Rocky Mountain states (Ferris and Brown 1981), 1768 m to 3200 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957; Emmel 1964; Scott and Scott 1978), to near sea level to at least 3048 m elevation in California (Emmel and Emmel 1962; Langston 1974), near sea level to more than 1981 m elevation in Oregon (Warren 2005). In Montana, reported from at least 13 counties in the southwestern 1/4 of the state, east to Carbon County (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993; FLMNH Lepidopterists' database; Butterflies and Moths of North America database), to at least 2134 m elevation. Mainly uncommon to common, rare in southern California (Glassberg 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on distribution by state, province, and country with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 3
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Moist to wet montane meadows, dry montane meadows, streambanks, forested roadsides, grassy woodland clearings, native grassland, oldfields, urban lawns (Emmel and Emmel 1962; Emmel 1964; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Pyle 2002; Warren 2005). Habitat in Montana not described but probably similar.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on host-plant Family and Genus associations with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
Food Habits
Larval food plants are grasses, but species used in the wild uncertain; in captivity include Festuca idahoensis, Poa pratensis, and Setaria glauca (Newcomer 1966; Scott 1986, 1992, 2006; James and Nunnallee 2011). Adults feed on flower nectar (including Astragalus, Berteroa, Calyptridium, Cirsium, Erigeron, Leontodon, Lotus, Melilotus, Rudbeckia, Taraxacum, Symphyotrichum), dung, and mud (Pyle 2002; Warren 2005; Scott 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females live 3-4 days in captivity, lay as many as 25 eggs, attempt to lay eggs on host plant leaves (eggs do not stick but fall to ground) or at base of host plant clumps (Newcomer 1966; Scott 1992; James and Nunnallee 2011). In captivity, eggs hatch in 7-8 days (depending on temperature), develop to L4 instar in 35 days, overwinter (diapause) as L4 instar, develop to L5 instar and pupae the following spring (Newcomer 1966; James and Nunnallee 2011); develop in lab from egg-laying to adult in 63-77 days (Scott 1992). Larvae feed on host plant leaves, build light silken shelters (L1 instar) and tubular nests of tied grass blades (L2-L5 instars), L4 instar wanders a few days before building strong silken cocoon and overwintering, pupate on or under the ground (Scott 1992; James and Nunnallee 2011). Males perch throughout the day in low spots of meadows at or near gound level to await passing females, perform courtship at flowers (Scott 1975b, 1982, 1986; Warren 2005; James and Nunnallee 2011).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Emmel, T.C. 1964. The ecology and distribution of butterflies in a montane community near Florissant, Colorado. American Midland Naturalist 72(2): 358-373.
Emmel, T.C. 1964. The ecology and distribution of butterflies in a montane community near Florissant, Colorado. American Midland Naturalist 72(2): 358-373. Emmel, T.C. and J.F. Emmel. 1962. Ecological studies of Rhopalocera in a High Sierran Community-Donner Pass, California. I. Butterfly associations and distributional factors. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 16:23-44.
Emmel, T.C. and J.F. Emmel. 1962. Ecological studies of Rhopalocera in a High Sierran Community-Donner Pass, California. I. Butterfly associations and distributional factors. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 16:23-44. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p.
James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Langston, R.L. 1974. Extended flight periods of coastal and dune butterflies in California. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 13:83-98.
Langston, R.L. 1974. Extended flight periods of coastal and dune butterflies in California. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 13:83-98. Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates. Newcomer, E.J. 1966. Life histories of three species of Polites. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 5:243-247.
Newcomer, E.J. 1966. Life histories of three species of Polites. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 5:243-247. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp.
Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1982. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. II. New observations and morphological adaptations. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 21(3): 177-187.
Scott, J.A. 1982. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. II. New observations and morphological adaptations. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 21(3): 177-187. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p.
Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128.
Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp. Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045.
Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Sonoran Skipper"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





