View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Bluegill - Lepomis macrochirus
General Description
Like all of the sunfish, the bluegill is native to central and eastern North America, not Montana. However, it is now found across most of eastern Montana. Similar to other sunfish species, the bluegill is a shoreline spring spawner. Males begin the nest-building by fanning the bottom with their fins to clear a shallow, bowl-like depression. Spawning is very temperature dependent, but when conditions are favorable a willing female lays her eggs in the nest. The male guards the nest tenaciously until the fry hatch out, and any type of intruder will be viciously attacked during the nesting season. All of the smaller sunfishes have been known to hybridize with other species and bluegills are no exception. Bluegill are the largest of the sunfishes other than bass and thus widely acclaimed as a sport fish in the Midwest. In Montana, they have grown to nearly 3 pounds, but they generally do not attain a size to make them a desirable sport fish. Consequently, fisheries managers who used to routinely stock bluegill in combination with bass, seldom do so in Montana today.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Gill rakers moderately long and slender. Ear flap smaller on females and young males than adult males. Young usually have vertical bars that become faint as adults.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
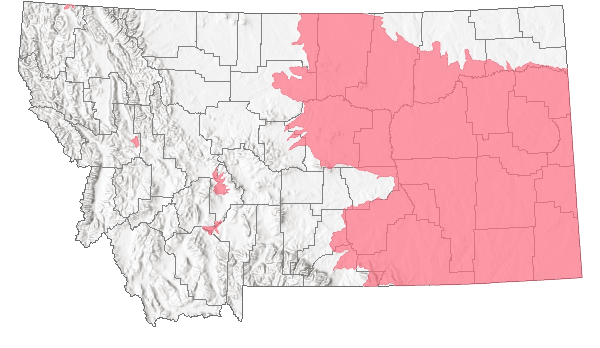
 Non-native
Non-native
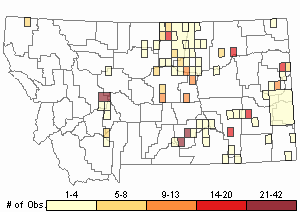
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 417
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
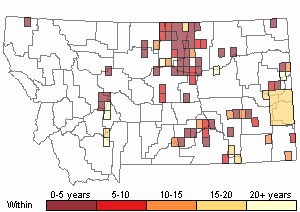
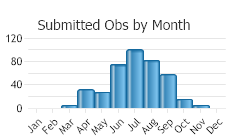
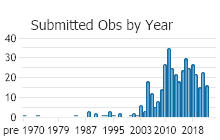
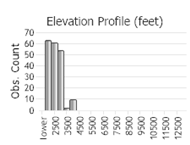 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Preferred habitat is comparatively warm lakes and ponds with abundant vegetation; also, in the quiet pools of streams.
Food Habits
Avid feeder. Eats mostly aquatic insects and other invertebrates throughout its life. Small amounts of aquatic vegetation and small fish are also taken by adults.
Ecology
Mostly found with other sunfish species in southeast Montana.
Reproductive Characteristics
Sexually matures mostly in 2 years. Spawns May - July after water temperatures exceed 68 degrees F.
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Craig, V.E. 1952. A story of fish production as it applies to Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 92 p.
Craig, V.E. 1952. A story of fish production as it applies to Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 92 p. Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p.
Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p. Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p.
Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p.
Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p. Stringer, A.L. 2018. Status of Northern Pearl Dace and chrosomid dace in prairie streams of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 150 p.
Stringer, A.L. 2018. Status of Northern Pearl Dace and chrosomid dace in prairie streams of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 150 p. Sundeen, D.R. 1968. Abundance and movement of young trout in a portion of the Madison River, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 19 p.
Sundeen, D.R. 1968. Abundance and movement of young trout in a portion of the Madison River, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 19 p. Sylvester, R. and B. Marotz. 2006. Evaluation of the Biological Effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment on the Fisheries Upstream and Downstream of Hungry Horse and Libby Dams, Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of EnergyBonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00 Contract No. 28350. 124 p.Contract No. 28350
Sylvester, R. and B. Marotz. 2006. Evaluation of the Biological Effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment on the Fisheries Upstream and Downstream of Hungry Horse and Libby Dams, Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of EnergyBonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00 Contract No. 28350. 124 p.Contract No. 28350 Sylvester, R. and B. Stephens. 2011. Evaluation of the physical and biological effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment upstream and downstream of Libby Dam, Montana. Libby, MT: Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of Energy Bonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00, Contract Nos. 43309 and 48555. 282 p.
Sylvester, R. and B. Stephens. 2011. Evaluation of the physical and biological effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment upstream and downstream of Libby Dam, Montana. Libby, MT: Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of Energy Bonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00, Contract Nos. 43309 and 48555. 282 p. Sylvester, R., A. Steed, J. Tohtz, and B. Marotz. 2008. Evaluation of the Biological Effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment on the Fisheries Upstream and Downstream of Hungry Horse and Libby Dams, Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of EnergyBonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00 Contract No. 28350. 124 p.Contract No. 28350
Sylvester, R., A. Steed, J. Tohtz, and B. Marotz. 2008. Evaluation of the Biological Effects of the Northwest Power Conservation Council's Mainstem Amendment on the Fisheries Upstream and Downstream of Hungry Horse and Libby Dams, Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks Annual Report prepared for U.S. Department of EnergyBonneville Power Administration. Bonneville Power Administration Project No. 2006-008-00 Contract No. 28350. 124 p.Contract No. 28350 USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p.
USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p. Wollitz, R.E. 1958. The effects of certain commercial toxicants on limnology of 3 cold water ponds near Three Forks, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 63 p.
Wollitz, R.E. 1958. The effects of certain commercial toxicants on limnology of 3 cold water ponds near Three Forks, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 63 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Bluegill"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Fish"





